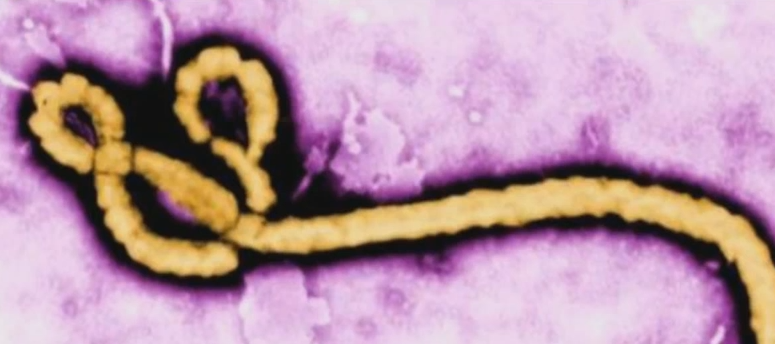
Is Ebola a virus or bacteria? This question often pops up, some say Ebola is a virus whereas few feel it is bacteria. The truth is ‘Ebola’ is a virus which is prevalent in African continent and also it has been affecting the people for many decades. Some of its symptoms of Ebola infection are organ failure, high fever with excessive bleeding; at times this disease can be fatal.
Ebola virus infection is a contagious condition found in animals. This virus is transmitted when a person comes in contact with the infected animal and once it enters a person, it spreads from one person to another through infected needle or bodily fluids.
At present people have no respite from this deadly disease, since it cannot be cured by medicines. Treatment for this includes supportive care and management of related health issues. Also, development of vaccine is in progress for Ebola virus; tests are currently being conducted in the United States of America by Center for Disease Control and Prevention for a vaccine.
Symptoms of Ebola virus
Symptoms usually occur within five to ten days after being infected by the Ebola virus. Some of the signs of Ebola virus are as follows:
- Muscle and joint pain
- Chills and fever
- Weakness
- Severe headache
As the infection increases/progresses, symptoms may deteriorate, which may be as follows:
- Red eyes
- Stomach pain
- Bloody diarrhea
- Nauseated feeling
- Chest pain
- Bruises
- Coughing
- Excessive weight loss
- Vomiting
- Hemorrhagic rashes, these may be high and uneven
- Internal bleeding
- Bleeding may occur frequently from the eyes. Bleeding may also occur from other open areas like ears, rectum and nose. This happens when the patient is in the last stages of severe Ebola virus infection. Mostly people suffering from this infection eventually die as a result of hemorrhagic fever.
The development of Ebola virus infection may become evident by the health problems given below:
- Excess bleeding
- Shock
- Jaundice
- Seizure
- Failure of multiple organs
- Hallucination
- Coma
Ebola virus infection damages the immune system directly, due to which it is unable to protect the body. This is one of the major causes for the high death rate linked with this infection. Doctors though are unaware as to why some people survive whereas others die.
Recuperation from this Ebola virus fever is very slow. The virus may be in the body of the patient for many weeks and to regain weight and strength may take time. Some other symptoms are visible too, these include:
- Loss of hair
- Inflammation of liver or hepatitis
- Headache
- Changes in sensory system
- Tiredness
- Weakness
- Inflammation of ocular
- Testicles inflammation
Causes of Ebola virus infection
Ebola virus breeds in primates which includes the African chimp, monkey etc. In Philippines a milder type of Ebola virus strain has been found to crop up in pig and monkey.
Transmission of the Ebola virus from animal to human:It is said that a man/woman can be infected by the Ebola virus when he/she comes in contact with the body fluid of an infected animal. Also the Ebola virus can spread if an infected animal is eaten or butchered. For e.g. when medical experts carried out operation on infected animal as part of the research, they also contracted the Ebola virus.
Transmission between humans:Ebola virus doesn’t transmit through air but it will spread when a person comes in direct contact of the body fluids of an Ebola virus infected patient. For example an infected person’s sweat, tears, vomit, urine, feces, blood, mucus, breast milk and semen come in contact with another person, the Ebola virus is transmitted. Normal contact with infected individual will not spread the disease, also as seen earlier it is not an air borne disease. It means that if an infected person sneezes or coughs it will not transmit the Ebola virus.
- Ebola infection is likely to be non-infectious till the time the Ebola virus patient experiences the signs and symptoms. When such an infected person coughs or sneezes, and the saliva or mucus comes in contact with the other person’s mouth, eyes, nose or any wound, then there is a high possibility of the Ebola virus to spread through these body fluids.
- Family members can easily be infected while caring for the sick. Medical experts are also at danger being infected by Ebola virus. This may happen when they treat Ebola patient without using protective gears such as mask, gloves etc.
Diagnosis of Ebola virus infection
Medical professionals may conduct following blood test to determine the presence of Ebola virus infection namely:
- Reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction or PCR
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay or ELISA
Treatment of Ebola virus
At present there is no drug available to cure the Ebola virus infection. Treatment therefore includes management and prevention of health complications as well as supportive hospital care like:
- Giving various fluids
- Oxygen being given as and when required
- Sustaining the blood pressure
- Treating other infections which may occur
Ebola is a virus not bacteria. It can be prevented if precautionary steps are taken such as regular washing of hands, keeping away from Ebola infected areas, using protective gear while treating Ebola infected patients or animals, avoiding direct contact with such patients and keeping away from bush meat.