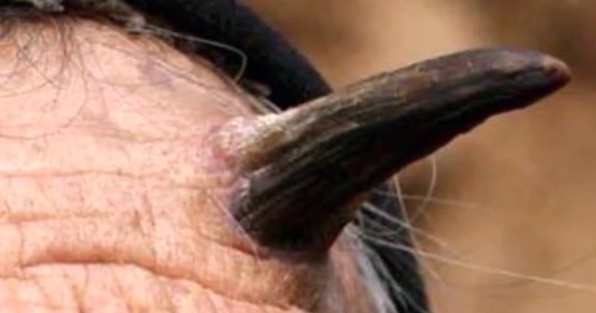
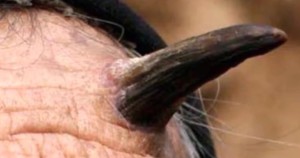
Keratin horn also referred to as cutaneous horn is a clinical diagnosis that refers to a projection of cornified material occurring above the skin surface. This conical projection resembles a small horn; hence its name. Keratin horn is made up of compacted keratin—the protein found in parts like the nails. The base of cutaneous horn may be flat, crater like, or nodular. Its size and shape may vary considerably but most of them are just a few millimeters in length.
The conical projections arise from benign, malignant or premalignant skin lesions. Squamous cell carcinoma is at times found at base of these horns. Although histologic lesions do occur at base of the horn, there is need for confirmation in order to rule out any possibility of a malignant growth. There are no clinical features that try to specifically distinguish between the benign and the malignant lesions.
However, bleeding and tenderness at base accompanied by lesions of large size in most cases could indicate malignancy. Keratin horns are commonly found in older people with a peak prevalence being witnessed in people of about 60 to 70 years in age. The horns are equally common in females and males but there is a higher risk of having a malignant base in men. Keratin horns are also common in people who have a skin phototype-1 and 2 or a fairer skin.
Appearance of a keratin horn
Most of the cutaneous horns are curved yellow to brown in appearance. They are hard because they are made up of compacted keratin. They have a border of skin, which is thickened, but they may also be surrounded by a normal skin. The horn can have some horizontal ridges resembling a terrace.
The keratin horn is taller than two times its width at base of skin but varies in length from a few millimeters to a couple of centimeters. In description, it looks like a miniature animal horn. The horns may occur singularly though at times, they may be several of them occurring anywhere on body.
Mostly, they are found in areas that are exposed to sun such as back of hands, forearms, ears, and head. The horns can also develop in other areas such as the neck, chest, and penis. About 40 percent of these cutaneous horns have lesions known as actinic keratoses, which are considered pre-cancerous.
Symptoms
Apart from the conical shape and protuberance that originates from a bump with red or pink to skin colored, there may be no other symptoms. However, an inflammation may occur at the base, which causes the skin where the horn originates to be tender. In some cases, rapid development or growth of the horn results in pain. There is a greater tendency of experiencing trauma because of the length or height, which may result in discomforts.
Causes of keratin horn
Keratin horns develop because of predisposing and precipitating factors. They show a tendency of developing to overly sun exposed body parts but they also grow in sun-protected skin. The growth of the horn starts from a process of hyperkeratosis in the skin surface, which is affected by hyper-proliferative lesion.
Most of the horns are as a result of development of common warts such as benign verruca or verruca vulgaris. They may also grow from benign skin growths like seborrheic keratosis. Unfortunately, others can grow from premalignant actinic keratosis. While most of these cases are benign, those developing from premalignant actinic keratosis are a concern because they indicate a near case of skin cancer.
There is a connection of keratin horn to human papilloma virus, which is associated with conditions like verruca vulgaris. Another virus, poxvirus or molluscum contagiosum has been linked to keratin horn growth.
Treatment
Surgical intervention is the common treatment for these cutaneous horns. This is the best treatment especially if there is presence of malignant growth. Many people who have this growth do not mind about it unless they are feeling uncomfortable. A person should always be conscious of the growth and should they feel something unusual such as tenderness, they need to see a doctor.
Having a keratin horn means that you could be at risk of developing cancer, though not always the case. Therefore, there is a need to be keen and look out for any signs of malignancy. Another problem is that there is no clear distinction of which keratin horn may be overlying a lesion considered to be benign or malignant. Only tests can indicate if there is susceptibility of cancer growth.
However, tenderness on the base of the horn has mostly been associated with malignancy. When a doctor finds an odd growth on the skin layer where the horn grows, it may be suspected as malignant. This is safe because it prompts a surgery procedure, which helps diagnose the skin underneath the horn to rule out possibility of precancerous or cancerous growth.
Brilliant post this match. I was checking constantly this vortal and Im ecciting! Extremely useful info specifically the last post 🙂 I was looking for this particular info for a long time. Thank you and good luck…