Cartilage is a flexible but stiff connective tissue occurring in varied body parts like the ear, joints, etc. It is not as firm or hard as bones, nor as flexible or supple as muscles.
Cartilage consist of extracellular matrix made of ground matter containing elastin fibers and proteoglycan as well as collagen fibers. The 3 main types of cartilage are fibrocartilage, hyaline cartilage, and elastic cartilage; each has varying levels of the major constituents.
Cartilage does not have blood vessels and gets its nutrition via the matrix. Repair and growth of cartilage is relatively slower than other connective tissues, leading to problems in easy healing of injured cartilage.
Hyaline cartilage has the largest share in the body. It occurs in diarthroidal joints which enclose long bones. Fibrocartilage has temporary presence at bone fraction locations. It permanent occurs in the knee meniscus, the spinal intervertebral discs, and as a cover of mandibular condyle present in temporomandibular joint. Elastic cartilage occurs in the Eustachian tube and the epiglottis.
Functions of cartilage
- Cartilage is essential in bone formation in growing infants. The tips of the long bones in legs and arms in young children have cartilage which slow convert into bones and grow bigger and longer.
- Some, such as rib cartilage, help hold together some bones and provide cover from shocks.
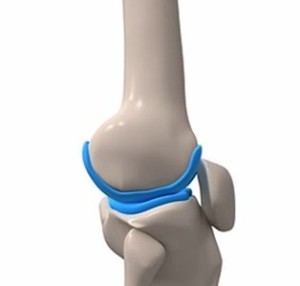
- In joints, cartilage acts as a cushion and prevents any friction of rubbing of the bones. For instance, the elbow and knee cartilage cushion the adjacent joints and help prevent joint pain.
- It is the only tissue in the body which keeps growing constantly. This is one of the reasons why the elderly have larger nose tips and larger earlobes. Both these regions feature cartilage.
- Hyaline cartilage cover the joint bones and facilitate their smooth motion. It mostly consists of type II collagen fibers. Fibrocartilage usually replaces damaged hyaline cartilage. However, as it is inflexible, it cannot bear any weight. Torn joint cartilage such as in the knee can be repaired quickly via the RICE method, i.e., rest, ice, compression, and elevation.
- The most flexible cartilage is elastic cartilage due to high elastin fiber content. It occurs in the larynx, outer ear, and the Eustachian tubes, etc. The impeccable balance of flexibility and structure offered by it is instrumental in keeping open the tubular structures.
- The most rigid and toughest kind of cartilage is fibrocartilage due to high collagen content, especially type I collagen which is stronger than type II collagen. It helps join ligaments and tendons to bones and also protects varied joints from varying levels of shocks. It occurs in the intervertebral discs and other regions with elevated stress.
Conditions of cartilage
Cartilage dysfunction often occurs due to damage of this connective tissue, which in turn can result in varied conditions, such as:
- Arthritis can develop due to joint cartilage degradation; arthritis is a condition marked by joint inflammation restricted motion, and intense pain.
- Ossification or transformation of cartilage into bone limits joint motion and can be classified under chondrodystrophies.
- Chondroma are non-cancerous tumors which occur in the cartilage.
- A cartilage defect called achondroplasia causes dwarfism.
I deliver in downtown Vancouver, Broadway, and sometimes
in Burnaby. Very shocked you turned down a door dash order, considering the snow has melted
and plus you have snow tires anyways
Feel free to visit my web page Skip The Dishes Referral Code
Где Вы ищите свежие новости?
Лично я читаю и доверяю газете https://www.ukr.net/.
Это единственный источник свежих и независимых новостей.
Рекомендую и Вам