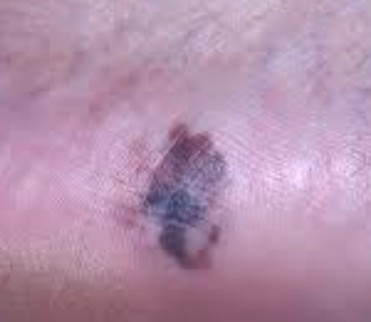
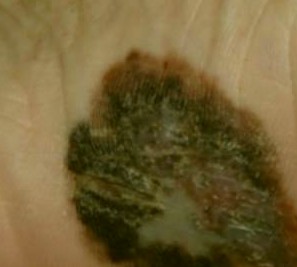
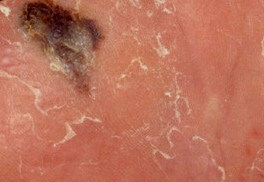
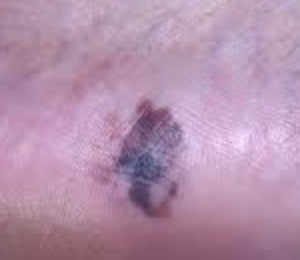
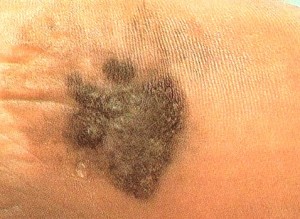
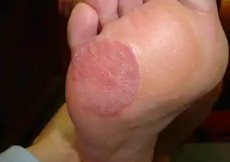
Acral lentiginous melanoma is a form of lentiginous skin melanoma, which occurs on the soles or palms. Melanoma is a serious skin cancer, which occurs in pigment cells or the melanocytes. It is common in people with dark skins. Acral lentiginous melanoma is commonly seen in areas such as soles, palms, under the nails, and on oral mucosa (mucus membrane coating the inside of mouth). It mainly occurs on the non-hair bearing parts of body, and these parts may be sun-exposed or not exposed to sunlight. Acral lentiginous melanoma occurs more on feet than on hands.
The cancer starts slowly by forming an enlarging flat patch, which is of discolored skin. Initially, the malignant cells tend to remain in the tissue of origin, for this matter, the epidermis. When in this stage, it is called the in-situ phase of the melanoma and it can persist for months or even years.
However, when the melanoma cells make their way across the basement membrane of epidermis, the cells enter the dermis, and the cancer becomes invasive. This is when a rapid growth tends to occur forming a nodular melanoma, which may proliferate and enter deep within skin. This form of cancer is found equally among females and males, and most of the people who have it are those over the age of 40.
Cause of acral lentiginous melanoma
The cause of this condition is unknown and it may not be related to sun exposure. However, it occurs when there is development of cancerous pigment cells along basal layer of epidermis. The cells can grow from previously normal-looking skin or from existing melanocytic naevus. The main cause however, may be attributed to gene mutations but is not clearly understood what causes the gene to mutate.
Appearance
The growth starts on melanoma within soles, fingers, palms and toes. It starts off with an enlarging patch consisting of discolored skin. One may think that, at first, it is a stain. At times, it can be amelonatic or non-pigmented assuming a red color. This kind of melanoma, like many other forms of this cancer, it may be recognized using the ABCDE rule which implies asymmetry, the border irregularly, the variation in color, a large diameter, and evolving in nature.
The size of the melanoma is usually more than 6 mm to several centimeters. The pigment may vary from brown, black, blue-grey, to red colorations. At first, the surface is smooth but later on, it becomes thicker and gets an irregular surface that may look dry and warty. Moreover, it may also ulcerate and bleed.
When it arises and forms on the nail regions, it is referred to as melanoma of nail unit. But when it starts within the nail growth areas, it is given the name subungual melanoma. On the nail plate, it may present in form of diffuse discolorations. It may also take the form of irregular pigmented longitudinal bands. In advanced form, it destroys the nail plate completely, and it can be amelanotic (without pigment or melanin).
What tests are performed to diagnose acral lentiginous melanoma?
A number of tests may be conducted when it is suspected that one has acral lentiginous melanoma. The tests include dermoscopy or using dermatoscope to distinguish it from other skin lesions such as moles, viral warts, and subungual haematoma or bleeding.
A biopsy of the skin lesion that is suspected to have this condition may also be done. A partial biopsy may be avoided unless it is a larger lesion; therefore, it is best to have excision biopsy. All in all, the diagnosis may not be easy and requires the right approach.
Treatment of acral lentiginous melanoma
Often, the initial treatment done on primary melanoma is to cut it out. There is need to completely excise the lesion using a 2-3 mm margin of the unaffected tissue. Other treatments may depend on the thickness of the lesion. When the biopsy is conducted, the radial excision margins may determine, which kind of treatment to follow such as flap or grafting to close exposed wound.
When the cancer has evolved from primary melanoma to subungual melanoma or acral lentiginous melanoma, a partial amputation may be done. When even after excision using wider margins of normal tissue, there is report of melanoma present in some parts, then other treatment may follow such as use of radiotherapy and more surgery procedures so that the tumor is removed completely.
Sometimes, the local lymph nodes may enlarge because of metastatic activity. This means that they may need to be removed. A surgical procedure may be required. Lymph nodes that contains metastasizing melanoma will usually grow in size quite quickly. Other forms of treatment may follow depending on how the lymph nodes have been affected and the amount of tissue involved. The doctor may monitor the patient to ensure that more follow-ups are made on treatment.
Acral Lentiginous Melanoma – Pictures
Накрутка Twitch Зрителей