Female dogs experience periods of quiescence and ‘heat’ in alternating cycles every eight to nine months. The ‘heat’ period is known as the estrus cycle and is marked by ovulation, external symptoms of ‘heat’, increased fertility and elevated sexual desire. It is followed by the diestrus period marked by impregnation of the female dog and hormonal changes that ready the body for pregnancy.
At the time of ovulation, the progesterone levels in female dogs tend to rise and remain that way, at almost the same levels and for almost the same period, irrespective of whether or not the dog has been impregnated or not. After the levels of progesterone start falling, there is a natural rise in the levels of another hormone called prolactin. Such normal hormonal changes and imbalances can make both the body and the mind of the dog to physiologically think that she has conceived. This condition is referred to as pseudocyesis, or phantom pregnancy, or false pregnancy in dogs.
Symptoms of false pregnancy in dogs
Some of the common signs and symptoms of false pregnancy in dogs are listed below:
Physical symptoms
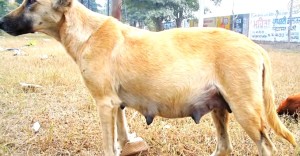
- The mammary glands may become enlarged. The teats tend to become tender and swollen.
- The abdomen may swell out; such enlargement of the belly may not be as big as observed during a real pregnancy.
- Occasionally, the female dog may also lactate milk or colostrum. Teats filled with milk may cause pain. A vet may then need to manually milk the teats to alleviate the pain. The duration of lactation and the severity of associated pain varies in different cases of false pregnancy in dogs.
- Elevated appetite with recurrent hunger pangs is common. It is also possible for affected dogs to lose all appetite and not eat food for many days.
- Incidences of morning sickness, which may sometimes be accompanied by vomiting and nausea, may be present. During such times, the dog may display changes in food habits; it may prefer bland food as compared to normal dog food.
- Some dogs may exhibit vaginal discharge, frequent urination, and fatigue.
Emotional/psychological symptoms
- Mood swings marked by increased aggression on one day and excessive lethargy the next. Increased stress as well as ongoing or oscillating episodes of depression may also be observed after the commencement of false pregnancy in dogs.
- The female dog will start mothering objects. She will take varied objects like soft toys, clothes, sock balls, etc. to her bedding area and start taking care of them.
- She may treat the toys as her puppies, become over-possessive and emotionally attached to such objects, and display strong maternal instincts towards them.
- Nesting is another common behavior seen during false pregnancy in dogs. The female dog will drag varied items like blankets, sheets, papers, cushions, etc., to a secluded place in the house and start building a nest for her ‘puppies.’
- She may become overprotective of her ‘puppies’ and may turn aggressive when people approach her while she is ‘mothering.’
Causes of false pregnancy in dogs
- The precise cause of false pregnancy in dogs is not known. Experts however believe that hormonal fluctuations, particularly of prolactin and progesterone, are instrumental in occurrence of the condition.
- It has also been observed that female dogs who have undergone an ovariohysterectomy, i.e., surgical excision of the uterus and the ovaries, also tend to elicit the abnormal symptoms associated with false pregnancy in dogs, 3 to 4 after the surgery.
Diagnosis
- There are no home pregnancy test kits for dogs. Pet owners need to take their pet to a vet in order to determine a case of false pregnancy in dogs.
- The doctor will carry out a variety of tests, including abdominal palpation, physical examination, radiographs, blood tests, X-rays, and/or ultrasounds to verify whether the dog is pregnant or not.
- It may be noted that false pregnancy in dogs has a tendency recur. Hence, it is easiest to diagnose in those dogs who have a history of the condition.
Treatment for false pregnancy in dogs
False pregnancy in dogs is normal; it is not a disease. The symptoms typically tend to disappear on their own in 2 to 3 weeks. Pet owners may however want to treat the condition as the abnormal symptoms may cause discomfort and distress to the dog. Pet owners are also likely to feel distressed by the abnormal state of their pet.
Treatment for false pregnancy in dogs include:
- Licking the engorged mammary glands can induce lactation. Hence, use t-shirts or Elizabethan collars to prevent such activity. According to some vets, reducing the daily food intake may also help decrease milk production.
- Discourage the ‘abnormal’ mothering behavior of the dog. You can do so by preventing her from creating a nest, admonishing the dog for such behavior, and taking away the surrogate puppies, i.e., the toys.
- Severe cases may need medical help. Medications can however cause side effects and hence have to be used as prescribed. A vet may recommend hormone therapy, mild tranquilizers, and diuretics; steroids for pain; sedatives for aggressive behavior; and prolactin suppressing drugs to reduce/stop milk production.
Pet owners who do not plan to breed their dog can go for sterilization to prevent future instances of false pregnancy in dogs.