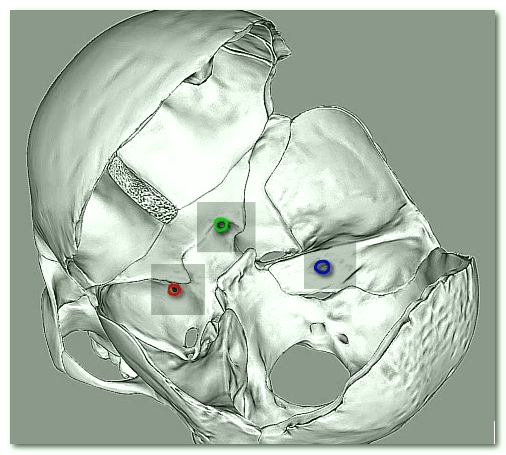
Foramen rotundum is a term used to describe a rounded hole or opening in the sphenoid bone of the skull, which in turn joins the pterygopalatine fossa and the middle cranial fossa. It transfers the trigeminal nerve’s maxillary nerve branch, the emissary veins, and the foramen rotundum’s artery
Foramen has its origins in Latin, wherein the word means an opening which looks like a hole. The term is derived from ‘forare’ which in Latin means to perforate or bore. The Latin word ‘rotundum’ means circular or round, indicating the rounded shape of the foramen rotundum.
Foramen Rotundum – Structure, development, and functions
Foramen rotundum is the name given to one of the many foramina or rounded apertures present at the base of the cranium, in the front and medial section of the sphenoid bone.
- The foramen rotundum is situated in the middle cranial fossa, at the lower medial end of the upper orbital fissure located at the inferior tip of the sphenoid’s greater wing. The sphenoid sinus’ lateral wall forms the medial border of the foramen rotundum. Also, the opening continues downwards and sideways in an oblique pathway and connects the pterygopalatine fossa with the middle cranial fossa.
- All through the fetal development process, the foramen rotundum constantly undergoes evolution with regards to shape. The process continues even after birth through to adolescence. The perfect circular ring-like shape of the aperture occurs after the fetus is 4 months old. During the fetal period, it is usually oval-shaped, while it becomes circular after delivery.
- As per varied studies, including the study published in the Anatomischer Anzeiger about the postnatal enlargement and topographical changes of the foramina rotundum, spinosum, and ovale, and the developmental study and research work done on the foramen rotundum, the foramen ovale, and the foramen spinosum and published in the Hokkaido Journal of Medical Science, the foramen rotundum tends to measure about 2.5 mm after birth, while it measures about 3 mm lengthwise in teens aged 15 to 17 years. It was also observed that the average diameter of the aperture tended to be about 3.55 mm in adults.
- The foramina rotundum does not have a significant mean area. This means that the aperture does not have any major role to play in the circulation of blood and other dynamics of the venous system present in the head. The V2 or maxillary branch of the CN V or trigeminal nerve goes across and exits the cranium via the foramen rotundum and the pterygopalatine fossa.