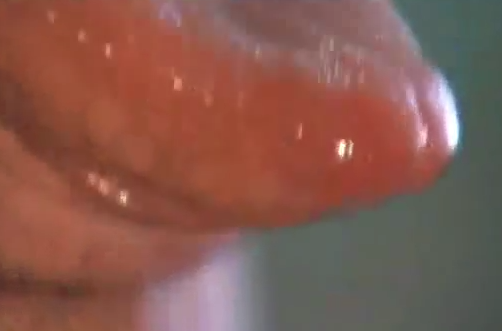
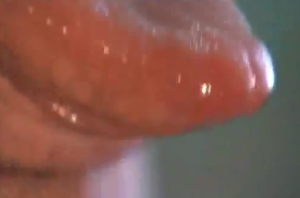
The taste buds are tiny finger-like structures that project out from the tongue. Enlarged or swollen taste buds can cause a lot of discomfort. If swollen taste buds are accompanied by infection, then the distress may be more intense. Swollen taste buds may be described as pale, painful, enlarged, and reddish, along with minor loss of function.
Taste bud functions
Food can be of varied flavors with the main flavors being salty, sweet, bitter, sour, and umami. Other flavors are usually a combination of all these main tastes. The taste buds present at the back of the tongue help recognize bitter flavors, the ones on the sides help gauge sour foods, and the taste buds at the tip are sensitive to salty and sweet foods.
Food that is consumed combines with saliva to help grind/chew it with the help of the teeth and tongue. Chemicals present in the food get released during this process of food breakdown, which are then sensed by the receptor flavor cells via the taste pores. The receptor cells get stimulated by the food chemicals and subsequently send impulses to the brain via nerves. The brain then interprets the taste of food that is eaten.
When the taste buds are swollen or inflamed, then the taste pores tend to get blocked. Consequently the receptor taste cells cannot detect the food chemicals and the brain thus cannot perceive the flavor of the food.
Causes
Some of the common causes of swollen taste buds on tongue are listed below:
- Consuming hot foods: Drinks and foods that are very hot as well as spicy foods may burn the taste buds, thereby scalding the tongue and causing the taste buds to become swollen.
- Oral infections: Different infections of the mouth and tongue such as oral thrush tend to irritate the oral lining and the mucous membranes. In such cases, the taste buds may also become infected, inflamed, and swollen.
- Exposure to alcohol, tobacco, or insecticides: Alcohol and tobacco contain potent chemicals which can irritate and inflame the nerves present on the tongue. Hence, excessive smoking or alcohol consumption can cause the taste buds on the tongue to become swollen. Pesticides also contain harmful chemicals. Even minor exposure to pesticides can adversely affect the tongue and the taste buds.
- Injury or physical trauma to the tongue: Burns, lacerations, cuts, and other physical injuries on the tongue can damage the tongue tissue, which may then cause the taste buds to swell up as well as elicit minimal functioning.
- Radiation therapy and/or chemotherapy: These therapies are treatments for different kinds of cancers. However, chemotherapy and radiation therapy can damage the mucous membranes, as they work by attacking cells that multiply rapidly, including normal healthy cells. The mucous membrane cells tend to multiply quite quickly and hence get attacked by the anti-cancer therapies. Thus, the mucous membranes become delicate; sometimes the entire mouth area, including the taste buds, may also become affected.
- Allergic reactions: Allergic reactions activated by the intake of foods that a person is allergic to causes increased buildup of eosinophil cells and other WBCs in the oral cavity, which can cause inflammation and swollen taste buds on tongue.
- Deficiency of vitamins and other nutrients: The health of the oral cavity is dependent on the supply of vitamin C and B complex. When these vitamins are not available sufficiently, then it can result in development of scurvy and other oral conditions that are marked by swollen tongue and inflamed taste buds.
- Potent mouthwashes, etc.: Use of strong mouth products with excess chemical content can also inflame the taste buds and mucous membranes. Vigorous tongue brushing can also damage the tongue papillae. Intake of certain medications can adversely affect taste buds function.
- Carcinoma: It is a type of cancer that damages the tongue’s normal cells and also destroys the taste buds.
- Acid reflux/GERD: If the stomach acid that is regurgitated is very strong, then the mouth may suffer from inflammation. Excessive gastric acids in the mouth can irritate the taste buds and cause swelling.
- History of mouth surgery: Laryngectomy, i.e., surgical removal of the complete larynx, and other similar oral surgeries can also sometimes cause swollen taste buds on tongue.
Treatment of swollen taste buds on tongue
- Oral infections caused by viruses, bacteria, and fungi are respectively treated with anti-viral, antibiotics, and anti-fungal medications. Consult a doctor for treatment.
- Vitamin nutritional deficiencies can be treated via intake of vitamin C and B supplements.
- Immediately consult a doctor if you feel that swollen taste buds are related to underlying malignancies.
Minor causes of swollen taste buds on tongue can be treated with the below listed home remedies:
- Gently pressured application of ice on the affected sections of the tongue can help alleviate swelling. Ensure that ice does not remain on the tongue for more than 2 minutes at a time, as that can limit the flow of blood to the tongue, thereby causing additional issues.
- Direct application of baking soda on the swollen taste buds will cool them down and reduce swelling. Baking soda can also be used to counter the effects of stomach acid regurgitated via acid reflux.
- Gargle with warm water saline solution 3 times a day. This will increase the flow of blood to the mouth, thereby reducing the inflammation. Do not use hot water to kill overgrowth of oral bacteria as it can scald the tongue.
- Mouth sores and oral injury or trauma can be healed via application of glycerin. Swollen taste buds on tongue will subsequently also ease up.
- A solution/mixture of pepper, garlic, and ginger can help alleviate bacterial infections of the mouth. Drink the solution at least 4 times per day.
- Honey has antibacterial qualities. You may rinse or drink honey to cleanse the mouth. It can also be directly applied on the infected tongue to alleviate underlying instances of swollen taste buds and the infection itself.
- Mix tea tree oil with warm water and gargle once a day to treat bacterial infections of the tongue. This home remedy should not be used frequently as excessive use can cause hallucinations.
Lifestyle changes like quitting smoking, limiting alcohol intake, regular exercise, as well as intake of a balanced and healthy diet can help prevent oral conditions and swollen taste buds on tongue.