Arrhythmia is a heart condition marked by dysfunction of the electrical impulses that control the rate of heartbeat, which can then result in rapid, irregular, or slower than normal heartbeats. Transient idiopathic arrhythmia is a term used to describe a condition of arrhythmia that occurs abruptly without any explicit known causes and vanishes just as spontaneously.
Most cases of transient idiopathic arrhythmia do not cause any significant harm to the health of the heart or the body. Patients usually experience the condition as a fluttering or racing heart. However, some forms of transient idiopathic arrhythmia may cause extensive distress and may even prove to be life-threatening
Transient idiopathic arrhythmia is treated by varied therapies that reduce, remove, and help control abnormal heartbeats. Presence of a weakened heart can increase the risk towards worsening of an underlying case of transient idiopathic arrhythmia. Hence, patients are advised to make some lifestyle changes and consume heart-friendly diets to decrease the instances of cardiac arrhythmia.
Symptoms
Transient idiopathic arrhythmia does not cause significantly visible or distressing signs and symptoms. Most cases of transient idiopathic arrhythmia are often diagnosed during a routine health checkup. It may also be noted that people with transient idiopathic arrhythmia may be prone to developing health problems like a stroke, heart attack, or cardiac failure.
There are a variety of cardiac problems that may accompany a case of transient idiopathic arrhythmia. They include:
- Signs and symptoms arising due to cardiac problems
- The chest region may experience sensations of fluttering
- The heartbeat may be slower than usual.
- Heartbeats that feel as if the heart is racing
- Symptoms arising due to reduced blood pumping by the heart.
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
- Unconsciousness or near fainting
- Lightheadedness or dizziness
- Generalized weakness
- Pain or discomfort in the chest area
Causes
The electrical impulses responsible for causing a heartbeat take a specific path across the heart system to create a contraction of the heart. Any type of disturbance in the path of these electrical impulses can trigger a case of transient idiopathic arrhythmia, or other types of cardiac arrhythmia.
In a normal healthy heart, a heartbeat occurs in the following manner:
- Contraction of the upper chambers of the heart. This allows the lower chambers to get filled with blood.
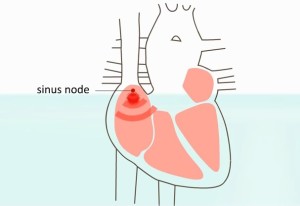
- An electrical impulse is released by the sinus node which then triggers both the upper chambers of the heart to contract.
- The electrical impulse passes to the center of the heart, down to the atrioventricular node occurring between the lower and upper cardiac chambers, and eventually into the ventricles.
- The complete process is carried out in a smooth manner in a normal heart, resulting in a resting rate of about 60 to 100 heart beats per 60 seconds.
There are some risk factors which can increase the susceptibility to transient idiopathic arrhythmia occurrence. They are listed below:
- Presence of coronary heart disease marked by clogged cardiac arteries.
- High blood pressure can increase the vulnerability to developing coronary heart disease. It can also trigger the walls of the left ventricle to thicken and become stiff, which then disturbs the normal flow of electrical impulses through the heart.
- Underling presence of different kinds of cardiac abnormalities, including cardiac trauma or damage, heart structure changes associated with cardiomyopathy, constriction of cardiac arteries, and valve defects, etc.
- Thyroid disorders such as hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can also trigger a case of transient idiopathic arrhythmia. Reduced thyroid hormone production can lower the metabolic rate, thereby causing the heartbeats to slow down or become irregular, while excessive thyroid hormones can hasten metabolism leading to racy or rapid heartbeats.
- Obstructive sleep apnea can hamper normal respiratory processes. Breathing disturbances can then slowdown the rate of heartbeats.
- Mismanaged instances of diabetes can cause coronary artery disease and hypertension, which may trigger a case of transient idiopathic arrhythmia.
- Caffeine and nicotine are stimulants which can speed up heartbeats and cause transient idiopathic arrhythmia. Hence, quit smoking and avoid the intake of excess coffee or caffeinated beverages.
- Use/abuse of cocaine, amphetamines, and other illegal drugs can cause extensive irregularity of the heartbeat; it not only poses an increased risk to occurrence of transient idiopathic arrhythmia, but also to the development of severe types of arrhythmia.
- Intake of certain kinds of prescription medications, OTC cough and cold medicines containing pseudoephedrine, and some kinds of diet supplements can also trigger a case of transient idiopathic arrhythmia.
- Presence of congenital heart defects increases the risk to irregular heartbeats.
- Increased consumption of alcohol can alter the pathways of the electrical impulses. Alcohol abuse for long periods of time can increase the risk to cardiomyopathy, abnormal cardiac function, and transient idiopathic arrhythmia.
- Different kinds of electrolytes occurring in blood such as potassium, magnesium, sodium, and calcium, etc., help activate and transmit the cardiac electrical impulses. Low or elevated levels of electrolytes can cause disturbances in normal flow of the impulses, resulting in transient idiopathic arrhythmia.
- Other risk factors of transient idiopathic arrhythmia include a previous instance of cardiac surgery; an ongoing episode of heart attack; scarring of cardiac tissue caused due to previous heart attack; and an electrical shock, some herbal treatments, air pollution, and stress.
Treatment of transient idiopathic arrhythmia
Most cases of transient idiopathic arrhythmia are mild and often do not require treatment. Lifestyle changes, regular exercises, and intake of a healthy, balanced diet are all that is needed.
Treatment may be required if transient idiopathic arrhythmia is accompanied by severe symptoms or if it comes with increased risk towards development of health complications. Treatment options include:
- Transient idiopathic arrhythmia marked by slower than normal heartbeats is remedied via use of a pacemaker.
- Transient idiopathic arrhythmia marked by racy or rapid heartbeats is corrected as follows:
- Use of prescription anti-arrhythmic medicines
- Use of an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator/ICD.
- Maze procedure, coronary bypass surgery, or other kinds of cardiac surgeries.
- Ablation therapy, wherein the portions of blood vessels responsible for causing transient idiopathic arrhythmia are ablated via use of one of more catheters with hot or cool tips.
- A variety of special procedures called vagal maneuvers can help reduce the rate of heartbeats. For example, straining or holding one’s breath, dunking the face in ice water, or coughing, etc.
- Cardioversion, wherein an electrical shock is administered to regularize the heart rate.
Well worth the $25.
Two things that I don鈥檛 really care about, but is worth mentioning, are 1) it has no pressure sensitivity and, 2) it is not able to activate the switcher bar or bring up the app dock.
Foot fatigue can play into how long you wear them and how long they are comfy.
The interior microphones in Bose QC25s are precision tuned for a specific air chamber: the one created by their own ear pads.
Classy yet different for a new summer look.
My only con is the cord length could be a bit longer.