Treacher Collins syndrome, also known as mandibulofacial dysostosis, is a rare genetic disorder. This condition affects the growth and development of bones and other tissues of the face. It is estimated to affect one in every 40,000 to 70,000 of live births. Most commonly, the chin bone and the lower jaw bones are affected, presenting as a small chin and small jaw. In rare cases, this condition may be accompanied by an improper fusion of the palatal bones, causing a gap in the palate, known as cleft palate. In extreme cases, bones may be so underdeveloped that they may cause interference with the airway of the infant causing life-threatening problem.
Clinical presentation (Signs and Symptoms)
Diagnosis is well established and obvious when the clinical features are completely apparent. Problem in diagnosis occurs when the signs are not completely expressed in the infant. The common presenting problems include:
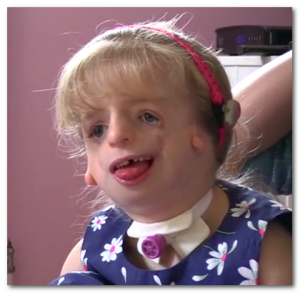
- Face: The facial features in this condition are characteristic for this, and are bilateral and symmetric usually. The nose is generally of the same size but appears larger because of the hypoplastic zygoma and supraorbital rim. The ear pinnae are malformed, varying in severity. The cheek bones are depressed and chin is receded, giving the mouth a down-turned appearance.
- Skull: The bones can be severity deformed, including hypoplastic growth of the malar bones, paranasal sinuses, zygomatic process and mandibular condyles. The orbits are hyperteloric, with deformation of the lateral margin. Cranial base is kyphotic while calvarium is usually normal.
- Eyes: Palpebral fissures show lateral curvature and are usually short. The cilia may be deficient from the medial side of the lower eyelid.
- Ears: The ear pinnae show malformations with crumbled appearance and forward curvature. Frequently, some other malformations of the middle ear may be present, including monopodal stapes, atresia of malleus or incus or absence of middle ear or tympanic membrane, all of which can result in hearing loss. The inner ear is normal usually.
- Throat and mouth: Presence of a cleft palate is seen in about one-third of the cases. Parotid glands may be absent or hypoplastic. The coronoid and condylar processes are also hypoplastic. Pharynx is invariably hypoplastic.
- Other dysfunctions: Mental status is usually normal. Tongue may show hypoplasia and may be placed backwards. Conductive hearing loss and impaired vision can also be seen.
Causes
- Embryology: This facial bones and tissues develop from the first and second branchial arches. It occurs due to the failure of neural crest cells to migrate to the first and second arches. The abnormality is therefore bilateral and symmetric. This occurs around the sixth or seventh week of the foetal growth. This period is crucial to avoid the development of this condition.
- Genetics: This condition has an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance. The mutation of TCOS1 gene is responsible for this condition to develop.
Treacher Collins Syndrome – Treatment
Various treatment modalities are used for the treatment of this condition and the choice of treatment depends upon the symptoms. Immediate care should be given to airway obstructions and swallowing difficulties.
Medical care:
If the airway is obstructed, tracheostomy should be done in the infant, which will be the source of air exchange for the newborn until the pharyngeal structures develop enough to clear the airway. A gastric tube may be required in patients who have swallowing difficulties. This is essential to ensure proper food intake and hydration of the patient. If substantial hearing loss is present, hearing aids should be fitted shortly after birth. It is important for the child for developing normal communication abilities and the initial bonding with family and relatives.
Surgical care:
The surgical methods are used according to the degree of deformity of the structure in concern and the time of correction is decided according to the physiologic requirement and comfort. The most concerning feature to be considered is the airway obstruction and deglutition problem. Both of these conditions occur secondarily to the mandibular retrognathism. For lengthening the mandible, distraction osteogenesis is being performed nowadays. This method is done by intubating the newborn at birth. The body of mandible is cut from both the sides and a distraction device in inserted in between the gap. Bone lengthening is done at the rate of 1-2mm per day. Extubation is done when the bone is lengthened upto 10mm.
Major obstructions of the airway are managed by tracheostomy while the minor obstructions are managed by lip tongue adhesion. This is done by surgically adhering lower lip with tongue and mandible. This maintains the tongue in the anterior position and avoids obstruction. Treatment of cleft palate is usually done at the age of 10-12 months but can be delayed if airway obstruction still persists. Other soft tissue abnormalities are treated according to the requirements and all the surgeries are done at lesser age so that healing repair and growth are normal, and also for the less appearance of scars.
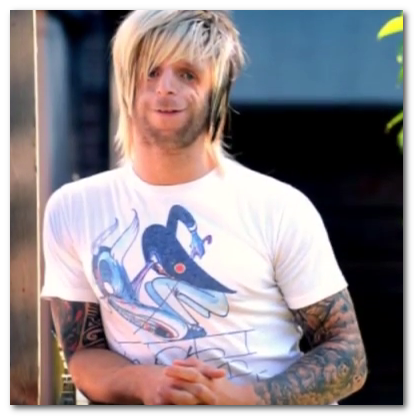
Treacher Collins Syndrome – Pictures
Treacher Collins Syndrome – Life Expectancy
Life expectancy is usually normal until the obstruction is so severe that it does not allow the child to breathe properly.




Требования к ставкам в casino x бонус также были снижены, для они соответствовали ожиданиям любителей, и тот случай, что они подразумевают ровно бонус, беспричинно и депозит, не беспричинно уж плох. У игроков Casino X не надо возникнуть проблем с отыгрыванием этой суммы 25 единовременно, только им следует запоминать, сколько игровые автоматы предпочтительнее, если они чувствуют, который период не для их стороне. Единоличный кошелек может заболевать мало заманчивым, и игроки будут склонны переводить средства, однако им следует воздерживаться через этого прежде тех пор, покуда бонус не будет получен.