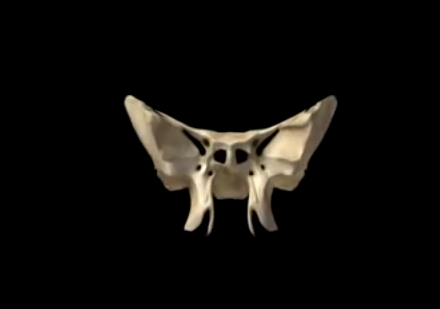
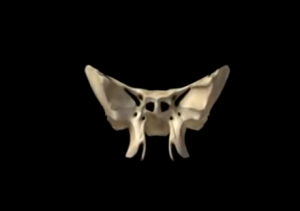
The sphenoid bone is one of the 8 bones that make up the cranium. It is a non-paired bone of the neuro-cranium. The shape of the sphenoid bone is quite interesting in the fact that it looks like the extended wings of a butterfly or a bat. The name is derived from the Greek word ‘sphenoeides’ which means wedge-like.
The sphenoid bone is located towards the front in the middle part of the skull, anterior of the temporal bone and near the bottom section of the occipital bone. It forms the cranium’s base, just posterior to the orbitals. The bone is regarded as one of the 7 bones which articulate to make the orbit.
Located bang in the skull’s center, the sphenoid bone features one of the most complex structures found in any bone occurring throughout the body. It consists of 2 greater wings, a median body, 2 pterygoid plates, and 2 lesser wings. The sphenoid bone primarily helps in the creation of the neuro-cranium base, the sides of the skull, and the floors. It also plays an important role in forming the walls of both the orbits which form the 2 cavities or openings containing the eyes.
The sphenoid bone – Anatomy and Functions
Functions: One of the main functions of the sphenoid bone is that it helps in the development of the essential anatomical structures and formations of the skull. The other important functions include the following:
- The bone consists of many fissures and foramina, which are oval or circular orifices via which arteries and nerves of the neck and head can travel through. For example, the maxillary nerve traverses across the foramen rotundum, the ophthalmic nerve travels across the superior orbital fissure, and the foramen ovale facilitates the passage of the mandibular nerve.
- The sphenoid bone poses as the perfect location for connection of the muscles that assist in the process of chewing food.
- It helps in the development of the lateral or side sections of the fossa and the skullcap.
Anatomy (In-Depth)
The sphenoid bone is made up of the following 4 structures:
- The median body: Also referred to as Corpus ossis sphenoidalis, the body is a section of the sphenoid bone that is shaped like a cuboid and situated in the middle. It features a total of 6 surfaces, i.e., the lower, upper, and back surfaces on each side. The body also consists of the sphenoid sinuses which is one of the 4 cavities of the skull that are filled with air and connected to the nasal orifices or cavity. The carotid sulcus, a canal like structure, is situated on either side of the medial body and acts as a passageway for the internal carotid artery. The body’s upper surface features the sella turcica, a big cavity that is home to the pituitary gland. The sella turcica consists of the tuberculum sellae on its anterior section, the square-like dorsum sellae posteriorly, the hypophysial fossa inside the sella turcica, and the posterior clinod process. The posterior clinoid process continues onwards on the right and left side of the dorsum sellae. The anterior and posterior clinoid processes surround the front and back wall of the sella turcica, respectively, around the pituitary gland. The thin ridge on the sphenoid bone called the sphenoidal crest occurs on the anterior section of the bone, while the sphenoidal conchae present on both the sides of the crest limit the opening of the sphenoid sinus.
- The 2 greater wings: Also known as Ala major, the greater wings of the sphenoid bone are bigger than the lesser wings. The bone plates of the greater wings bend in the upward direction, to the back and side. They help in creation of the floor and the middle cranium’s lateral wall. They start with a wide base located at the lateral surface of the body of the sphenoid bone. Each of the greater wings consist of 4 surfaces, i.e., orbital, cerebral, maxillary, and temporal. The cerebral surface facing the cavity of the cranium features the foramen rotundum, a circular opening which acts as a passageway for the trigeminal nerve’s maxillary nerve branch. It is medial and anterior to the foramen ovale, an oval orifice via which the mandibular nerve, the lesser petrosal nerve, the accessory meningeal artery, and emissary veins pass through. The foramen spinosum lies at the back portion of the foramen ovale. The mandibular nerve’s meningeal branch and the middle meningeal artery pass across the foramen spinosum. The orbital surface of the greater wings forms the lateral or side wall of the relative orbit, while the temporal surface is home to the infra-temporal crest.
- The 2 lesser wings: Also known as Ala minor, the lesser wings are the smaller of the 2 triangular-shaped, flattened, wing-shaped plates of bone that project out on the lateral or side surface on either side of the sphenoid bone’s body. The pair or greater wings are located below the lesser wings. At the bottom section of the lesser wings, one can find optic canal which pass and continue onwards into the ocular orbits. The lesser wings constitute a small portion of the orbit’s medial back wall and their non-used rims act as a margin between the middle and anterior cranial fossae. The anterior edges of the lesser wings are joined to the frontal bone’s orbital portion as well as with the ethmoid bone’s cribriform plate. A narrow orifice situated between the lesser and greater wings and known as the superior orbital fissure extends diagonally across the posterior section of the orbit. The trigeminal, oculomotor, abducens, and trochlear nerves run across the fissure. The ophthalmic artery and the optic nerve run across the optical canal situated along the lesser wings.
- The 2 pterygoid processes: Also known as Processus pterygoideus, the pterygoid processes are 2 bony processes that extend downwards from the intersection of the sphenoid bone body and the greater wings. At the bottom section of each of the pterygoid processes, a pterygoid canal runs posteriorly to anteriorly. Each process consists of a medial and lateral plate. Pterygoid fossa refers to a depression occurring between the medial and lateral plates. The lateral pterygoid muscle, instrumental in mandible movement during chewing, joins the lateral plate. The muscles that help swallow attach to the medial plate. The pterygoid hamulus, a medial plate hook-like extension, also assists in swallowing processes.
What’s up, after reading this amazing post i am also happy to
share my experience here with colleagues.
Excellent post. I was checking continuously this weblog and
I am inspired! Very helpful info specially
the ultimate phase 🙂 I take care of such info much. I used to be seeking this particular info for a
long time. Thanks and best of luck.
I’m not that much of a internet reader to be honest but your blogs really nice,
keep it up! I’ll go ahead and bookmark your site to
come back later. Many thanks
Hey! I know this is somewhat off topic but I was wondering which blog
platform are you using for this site? I’m getting fed up of WordPress because I’ve had issues with hackers and I’m looking at alternatives for another platform.
I would be awesome if you could point me in the direction of a good platform.
Heya! I understand this is kind of off-topic but I had to
ask. Does running a well-established website like
yours require a lot of work? I’m brand new to writing a blog but I do write
in my diary on a daily basis. I’d like to start a blog so I can share
my experience and views online. Please let me know if you have any
recommendations or tips for brand new aspiring
bloggers. Appreciate it!
Do you mind if I quote a few of your posts as long as
I provide credit and sources back to your site?
My blog is in the exact same area of interest as yours and my
visitors would definitely benefit from a lot of the information you provide here.
Please let me know if this alright with you. Thank you!
Marvelous, what a webpage it is! This blog provides useful
information to us, keep it up.
Currently it looks like Expression Engine is the best blogging platform availableright now. (from what I’ve read) Is that what you areusing on your blog?
You should be a part of a contest for one of the most useful websites on the internet.
I am going to highly recommend this website!
Wow, wonderful weblog format! How lengthy have you been running
a blog for? you make running a blog look easy. The total look of your site is great, let alone
the content material!
I visit every day some websites and blogs to read content, but this weblog givesfeature based writing.
I am curious to find out what blog system you are utilizing?I’m experiencing some small security issues with my latest site and I’d like to find something more secure.Do you have any solutions?
Hello, i think that i saw you visited my site thus i came to “return the
favor”.I am attempting to find things to improve my website!I suppose
its ok to use some of your ideas!!
I’ve been surfing online greater than three hours today, yet I by no means found any fascinatingarticle like yours. It’s beautiful price enoughfor me. In my view, if all web owners and bloggersmade excellent content as you did, the internet shall bea lot more useful than ever before.
Hi there! I simply would like to give you a huge thumbs up for the great info you have right here on this post.
I am returning to your website for more soon.
Attractive section of content. I just stumbled upon your weblog and in accession capital to assert that I
acquire actually enjoyed account your blog posts. Anyway I
will be subscribing to your feeds and even I achievement you
access consistently fast.
Attractive component to content. I just stumbled upon your site and in accession capital to
claim that I get actually enjoyed account your weblog posts.
Any way I will be subscribing on your augment and even I success you get
admission to persistently fast.
Hello there! Would you mind if I share your blog with my twitter group?
There’s a lot of people that I think would really appreciate your content.
Please let me know. Thanks
I do trust all of the ideas you have presented to your post.
They’re really convincing and can certainly work. Nonetheless, the posts are
very brief for beginners. May you please lengthen them a bit from
next time? Thank you for the post.